Diamond Buying Guide: Understanding the GIA 4 C's
Purchasing a diamond, whether for an engagement ring, an anniversary gift, or a personal indulgence, is a significant decision. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) has developed a standardized method to assess diamond quality known as the 4 C's: Carat, Cut, Color, and Clarity. Understanding these four aspects will equip you with the knowledge needed to make an informed purchase.
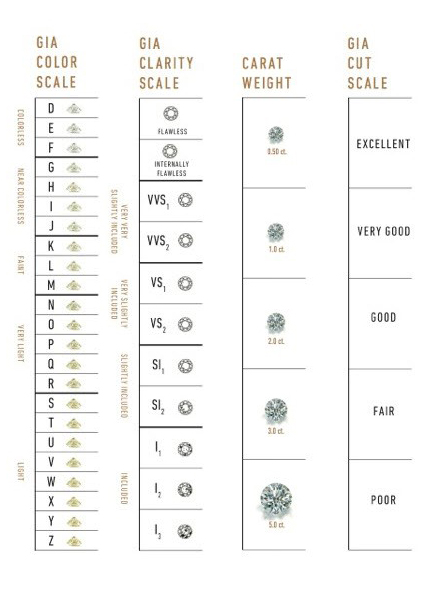
GIA Diamond Grading Scales
How to read a GIA diamond grading report
1. Color
Color in diamonds is graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
- Diamonds at the D, E, and F grades are considered colorless, with premium pricing.
- As you move down the scale, the diamond has a more noticeable color, which usually decreases value unless you're looking for a fancy color diamond.
- Fancy color diamonds, like blues, pinks, or yellows, are valued differently and follow their unique grading system.

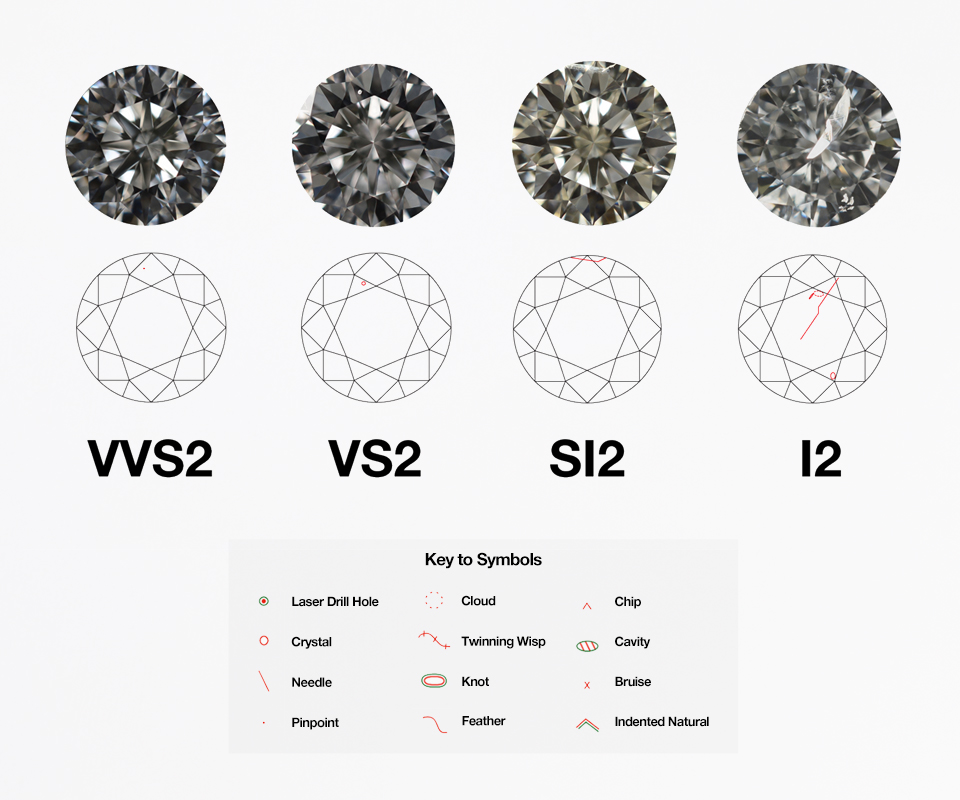
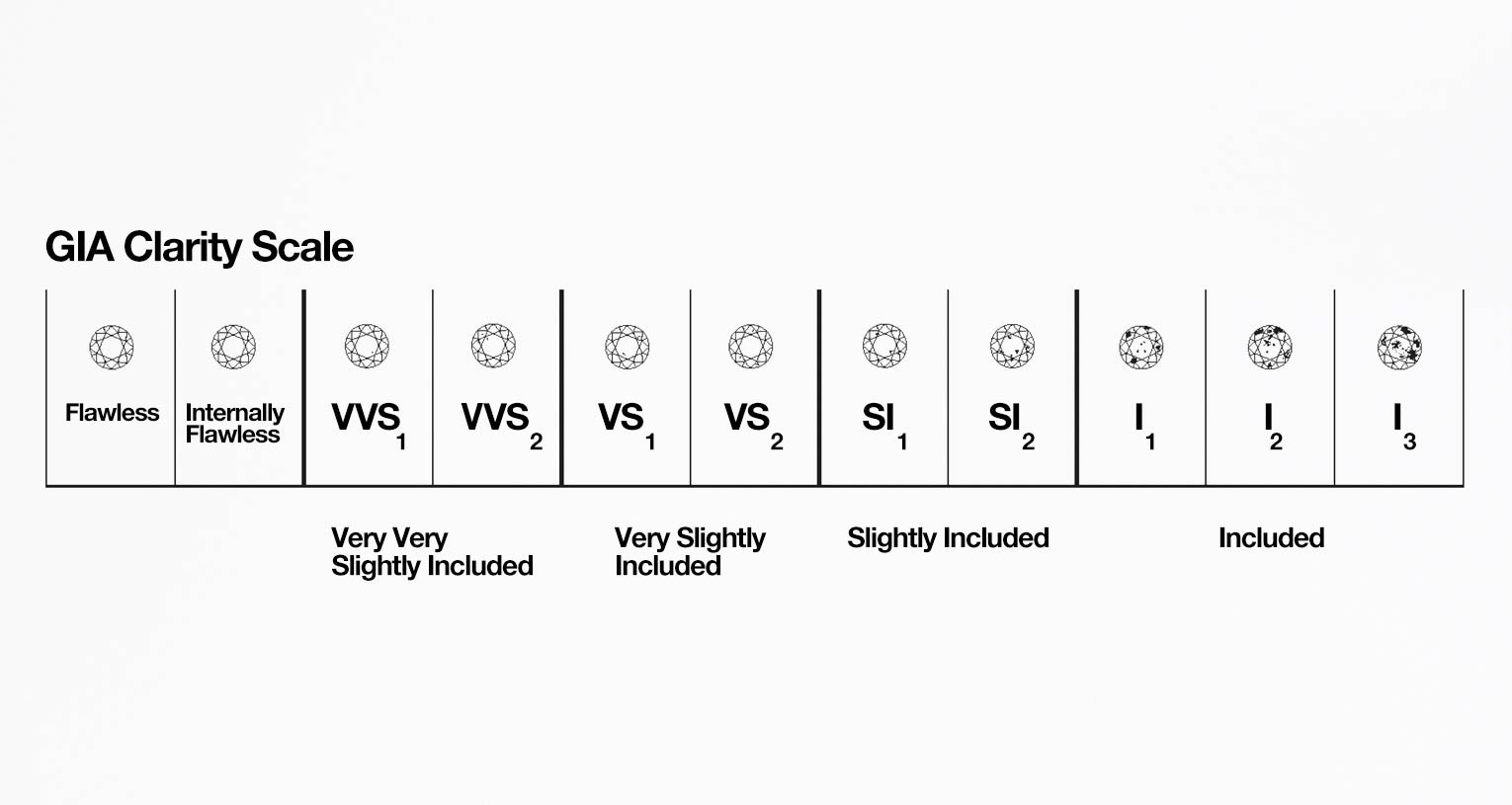
2. Clarity
Clarity measures the presence of inclusions (internal flaws) or blemishes (external flaws) in a diamond.
- Grades range from Flawless (FL) to Included (I1 to I3).
- Most diamonds have inclusions, but those that are "eye-clean" (inclusions not visible to the unaided eye) offer great value without compromising beauty.

3. Cut
The Cut of a diamond is the most complex of the 4 C's because it impacts how light interacts with the stone, affecting its brightness, fire, and scintillation.
- Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, and Poor are the grades for cut quality.
- A well-cut diamond reflects light internally from one facet to another, leading to a dazzling display of white light when viewed from the top.
- A poorly cut diamond might leak light through the sides or bottom, making the stone appear darker and less vibrant.
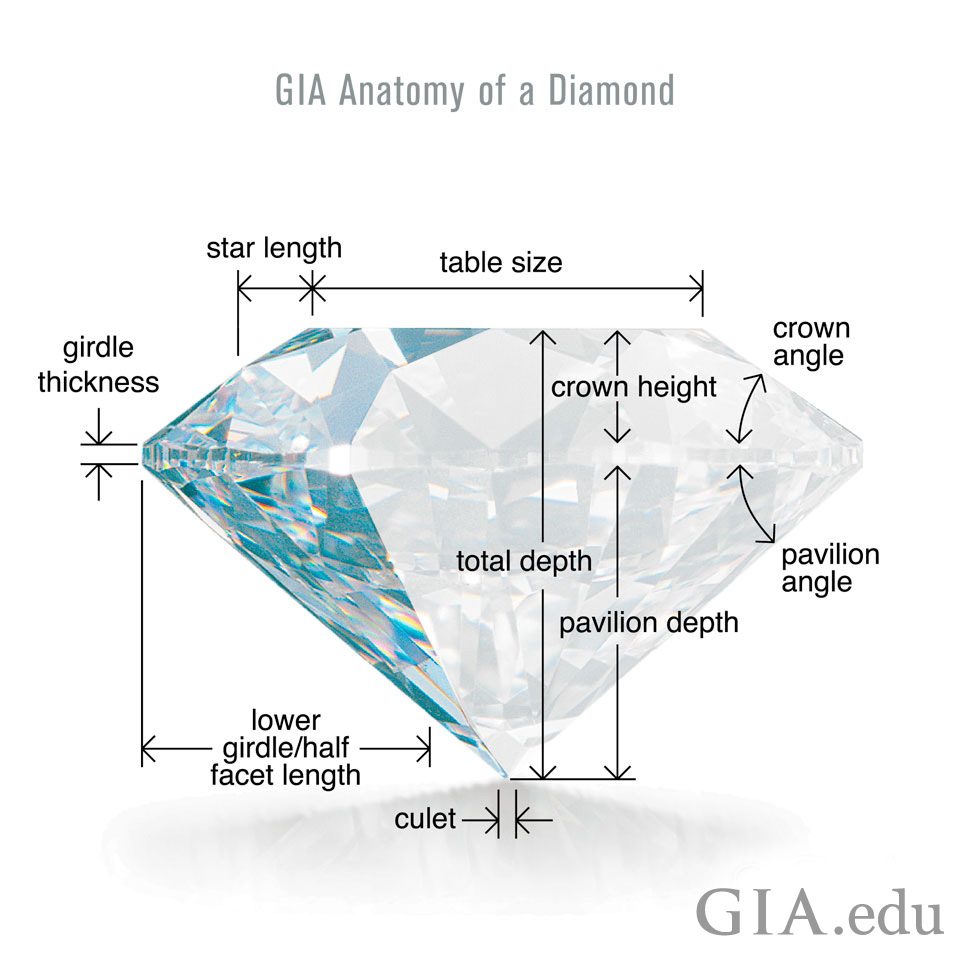
This graphic illustrates the proportions that affect a diamond’s cut grade. The crown and pavilion angles and the relative measurements of its facets contribute to a diamond’s brightness, fire, and scintillation.

Diamond Cuts: Shallow, Deep, and Ideal
The cut of a diamond significantly influences its brilliance, fire, and overall appearance.

Credit by Hendricksons Jewelry
Shallow vs. Deep vs. Ideal: At a Glance
| Feature | Shallow Cut | Deep Cut | Ideal Cut |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brilliance | Low | Low | Maximum |
| Light Reflection | Escapes from the sides | Absorbed or leaks out | Fully reflected back |
| Size Appearance | Larger than carat weight | Smaller than carat weight | True to carat weight |
| Popularity | Less preferred | Less preferred | Most sought after |
When choosing a diamond, prioritize the ideal cut for its unparalleled brilliance and fire. While shallow and deep cuts may tempt buyers with lower prices or perceived size, they lack the visual appeal and elegance of a well-cut diamond.
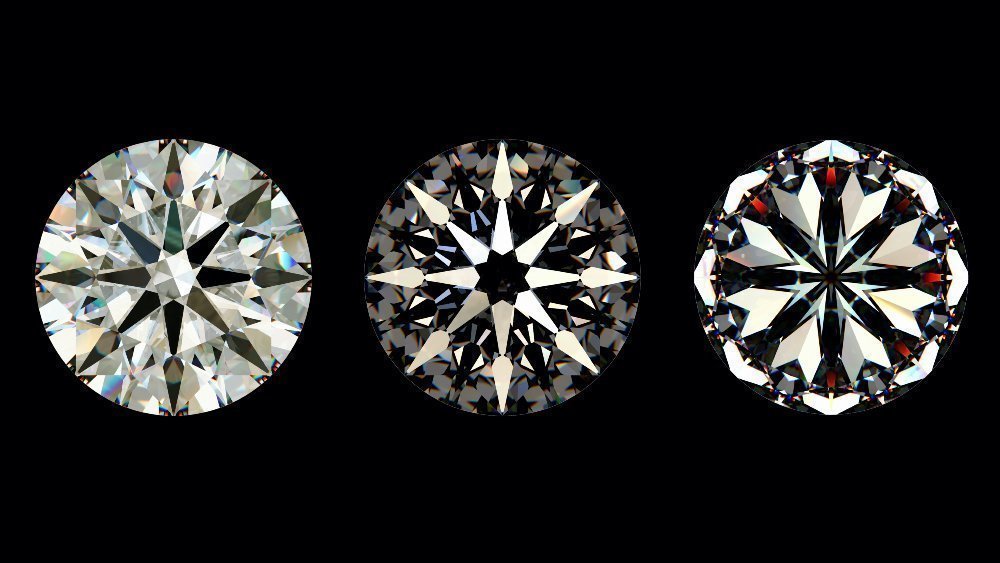
Hearts and Arrows Diamond Cut
The Hearts and Arrows Diamond Cut refers to a specific and highly precise cutting style that achieves exceptional symmetry, brilliance, and fire. When viewed under a specialized viewer or scope, a perfectly cut Hearts and Arrows diamond will reveal:
- Hearts: Seen from the pavilion (bottom) of the diamond, this pattern shows eight symmetrical heart shapes.
- Arrows: Seen from the crown (top) of the diamond, this pattern reveals eight perfectly aligned arrowheads.


4. Carat
Carat Weight refers to the size of the diamond. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams. However, carat weight alone does not determine value; two diamonds of equal carat weight can have very different prices based on the other C's. Remember:
- Larger carat weights are rarer and thus more expensive.
- Proportions matter; a well-proportioned smaller diamond might look larger than a larger, poorly cut one.

Tips for Buying:
- Certification: Always opt for diamonds with a certificate from reputable institutes for an unbiased quality report.
- Light Performance: Consider how the diamond looks under different lighting conditions.
- Proportions: Even for carat weight, ensure the diamond has balanced proportions for optimal sparkle.
- Budget: Decide how much you want to spend and understand where you can compromise if necessary (e.g., slightly lower color or clarity for a better cut).
Top Reputable Diamond Grading Institutes:
- Gemological Institute of America (GIA): The leading institute globally, renowned for its stringent and detailed diamond evaluation standards. GIA's certificates are widely recognized and highly valued for their reliability.
- American Gem Society (AGS): AGS also provides diamond certificates with high standards, particularly emphasizing cut quality. Their grading system can offer additional insights into light performance and brilliance.
- Hoge Raad voor Diamant (HRD): Based in Antwerp, Belgium - the diamond capital of the world, HRD provides high-prestige certificates, especially in the aspects of cut and color grading.
- International Gemological Institute (IGI): Known for detailed certifications and quick service, IGI is suitable for buyers needing a fast report.
- European Gemological Laboratory (EGL): While not rated as strictly as GIA or AGS in terms of grading stringency, EGL remains a popular choice, particularly in some markets.
When buying a diamond, ensure you have a certificate from one of these reputable institutes to guarantee quality and value.
How to choose a diamond
Conclusion
When buying a diamond, remember that each 'C' interplays with the others. A diamond with an excellent cut can enhance the appearance of color and clarity, potentially making a lower-carat weight or less perfect color diamond still spectacular.
Education is your best tool; armed with knowledge of the GIA 4 C's and an awareness of reputable grading institutes, you'll be better prepared to select a diamond that will be cherished for a lifetime.




